Water Trash Removal
Origin
A research report on river-borne plastic debris flowing into the seas, issued by the Ocean Cleanup in June 2017, indicated that 1.15 to 2.41 million tons of plastic debris are brought into the ocean every year by over 40 thousand rivers investigated in the research around the world, and the top 20 rivers contributed 2/3 of the total amount.
Individuals or businesses emit wastewater or dump debris directly into rivers, causing water pollution or accumulation of debris, undermining flow of water, flood discharge, ecology and water quality of the rivers, and even the environment and ecology to which the general public is a part of. The debris eventually flows into the seas along with rivers, causing marine pollution.
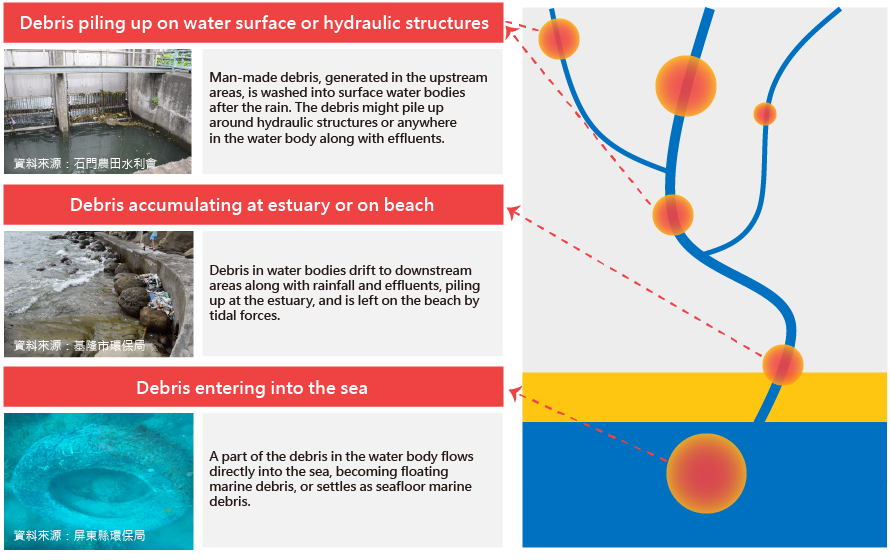 Causes of water body debris pollution
Causes of water body debris pollution
People creates garbage at upstream. The garbage is washed off by rainwater into surface water bodies, and carried by runoff until it is stopped by hydrologic structures and along the water bodies. At downstream, it accumulates at estuaries and eventually tides carry it to beaches. Some of the water body garbage is carried to the ocean and becomes drifting garbage on the surface or sinks to the bottom of the ocean.
The Ministry of Environment (MOENV) (formerly EPA), dedicated to the reduction of marine debris, promoted a vision of “Plastic Free Ocean” and formed Marine Debris Governance Platform jointly with NGOs in 2017. The alliance proposed Action Plan of Marine Debris Governance in Taiwan in 2018, by which EPA planned to manage “debris containment and disposal in surface water bodies around the country” to prevent “land-based debris entering into the seas.”
 vision of “Plastic Free Ocean” proposed by the MOENV
vision of “Plastic Free Ocean” proposed by the MOENV
EPA has a vision of “plastic-less ocean.” The idea is the effective management of ocean garbage through control at source, garbage reduction and cleanup at ocean hot spots, as to promote the plastic-less ocean through plastic cleanup and restriction. The ocean waste remedy platform was established in July 2017 with the participation of EPA and relevant NGPs in the country. It is established based on the principle of cooperation between governmental and private sectors with the aim to continuously influence stakeholders of ocean wastes.
Implementation
(1) incorporating universities, colleges, communities, enterprises and organizations to implement a series of water body protection campaigns
the MOENV organized beach-cleaning or river-cleaning campaigns. Nowadays it further collaborated with Water Resources Agency, Department of Irrigation and Engineering and local governments to jointly reduce land-based debris.
River guards cleaning the river water and riverbank, two pictures.
(2) Management of containment and disposal of debris in surface water bodies
the MOENV, in accordance with the law, manages 5 water bodies where debris is most likely to pile up: rivers, regional water drainage, rainwater drainage, side drains and canals.
Competent authorities governing water bodies in local governments inspect water bodies and implement containment and disposal operations regularly. They start by understanding the basics of debris in water bodies and then analyze possible causes of pollution hotspots, so to deploy appropriate resources for containment and disposal operations, and build a joint defense system across departments. Given that many departments are involved in the management of water bodies, the MOENV took the initiative to negotiate with different departments to form consensus, systemize and integrate resources, so to strengthen routine management practices of each department and to collectively stop land-based debris from flowing into the seas. These practices include:
1. Patrol
Timely report when debris is spotted during field investigation, and undertake containment and disposal operation
Build water body debris background information through long-term inspection, two pictures.
2. Containment and disposal
Classify debris regularly to understand the composition of debris.
containment and disposal operations are undertaken by each water body governing authority regularly or irregularly, two pictures.
the MOENV inviting concerned departments to form partnerships, two pictures.
Results
To achieve the goal that “no land-based debris enters into the seas,” the MOENV encourages all water body managing departments to go online and report the amount of water-borne debris contained since 2019. From January 1st to August 31st, 2019, 130,989 tons of debris have been cleaned, showing a significant average increase comparing with the amount in the past years. These debris went through 1,041 classification operations, and most of them were sludge, common water hyacinths, weed plants, bamboos and tree branches. In addition to sludge, weed plants, common water hyacinths, bamboos or tree branches that might obstruct the waterways, the debris in the surface water bodies was mainly composed of man-made waste, such as packed garbage (70.1%), plastic waste (13.65%) and glass (7.88%). Please refer to the following table for more details. Most of the debris were part of household waste.
A total of 5,103 water body containment and disposal stops were put in place for 2,251 water bodies around the country. Each stop is equipped with bumps, intercepting gates, bridge piers or incoming drainage ports. From January 1st to August 31st, 2019, these stops contained and disposed 5007.2 tons of debris from water bodies, with another 125,981.8 tons removed from non-fixed locations. In 2018, the country has 428 water environment patrol teams, composed of 12,018 members. They were engaged in 3,718 river cleaning operations and cleaned a total of 410 tons of debris.
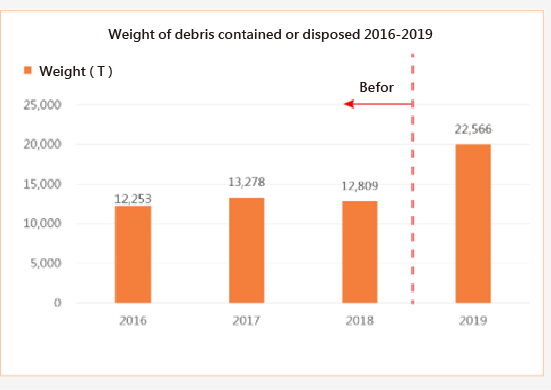 Total amount of debris contained or disposed 2016-2019
Total amount of debris contained or disposed 2016-2019
The water trash removal has been in place since 2016. Every year, more than 10,000 tons of trash are removed and this number reached even higher at 22,566 in 2019.
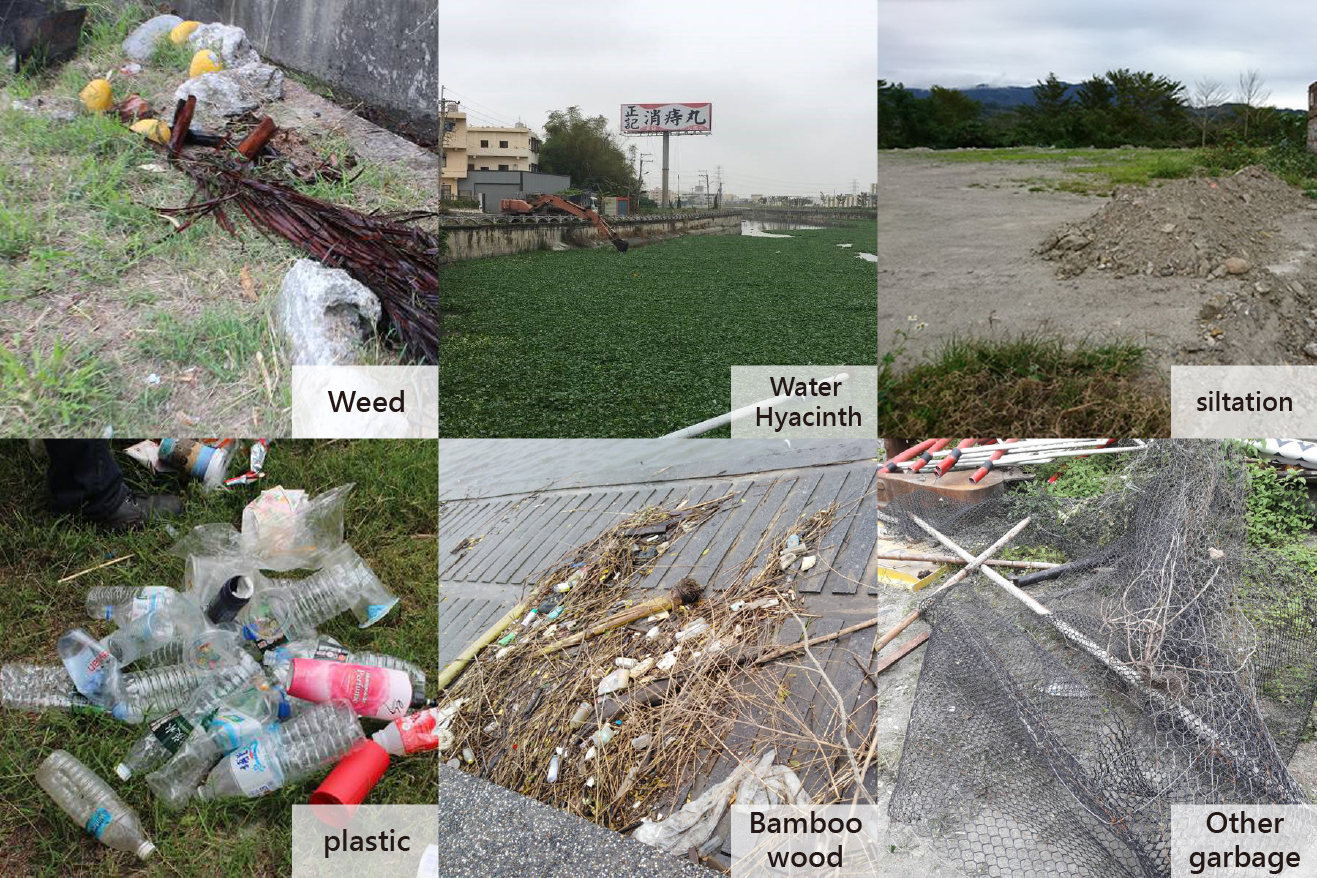 man-made and natural debris in the water bodies on land
man-made and natural debris in the water bodies on land
Garbage found in land-based water bodies, both 21z and manmade, includes: weed, water hyacinth, siltation, plastics, bamboo woods, and other garbage.